Whether you’re training a large team or deploying on-site across multiple locations, we will craft a bespoke package. Volume discounts and corporate rates are available.
Real Estate Agents

Aerial Property Photos & Video
- Capture wide-angle, bird’s-eye views of properties.
- Highlight land size, nearby roads, surroundings, and landscape.
- Showcase luxury homes, large estates, commercial spaces, or rural properties more effectively than ground-level shots.
Virtual Tours & Cinematic Walkthroughs
- Drones can smoothly fly through a house or around a property, giving potential buyers a dynamic tour experience.
Marketing & Promotion
- High-quality drone footage enhances listings on MLS, Zillow, and social media.
- Videos often get more engagement than static photos.
Site Planning & Development
- For developers and investors, drones help with topographic surveys, progress tracking, and site mapping.
Photography Use of Drones

Unique Angles and Creativity
Photographers can shoot from high above or unusual angles to add drama and context to images—impossible with handheld cameras.
Event Photography
Perfect for weddings, festivals, or outdoor events to capture sweeping crowd or venue shots.
Cinematic Video Footage
Drones enable smooth tracking shots, panning, and fly-through that elevate any video production.
Time-Lapse and Mapping
Some drones offer advanced features like automated flight paths for mapping or capturing time-lapse scenes from the air.
Construction and Surveying Professionals

Site Surveying and Mapping
- Create accurate topographic maps and 3D models using drone photogrammetry.
- Speed up land surveys compared to traditional methods.
Project Monitoring and Progress Tracking
Capture regular aerial photos or videos to track the progress of a build.
Share updates with stakeholders, clients, or remote teams.
Inventory and Material Management
Count materials like sand, gravel, or lumber through aerial imaging and volume measurements.
Reduce theft and wastage by monitoring storage areas.
Safety and Inspection
Inspect hard-to-reach areas like roofs, towers, or scaffolding without endangering workers.
Identify hazards early (unstable ground, water accumulation, etc.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) Integration
Overlay drone data on BIM models to verify accuracy and detect deviations.
Use of Drones in Land Surveying

Site Surveying and Mapping
- Create accurate topographic maps and 3D models using drone photogrammetry.
- Speed up land surveys compared to traditional methods.
Topographic Surveys
Collect elevation data quickly for use in site planning, drainage analysis, or road design.
Volume Calculations
Measure cut-and-fill volumes for earthworks or stockpile management.
Boundary and Property Surveys
Combine drone imagery with GPS/GNSS ground control for highly accurate boundary mapping.
Use of Drones in Agriculture (Precision Farming)
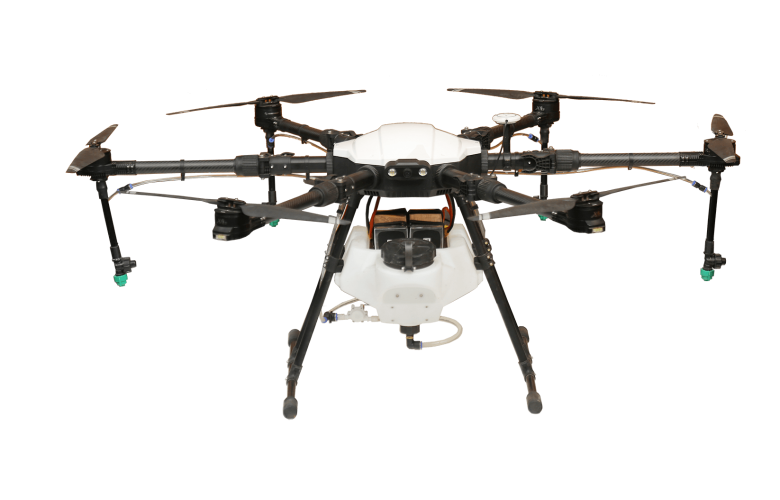

Crop Monitoring & Health Assessment
- Use multispectral or NDVI cameras to detect crop stress, disease, pests, or water deficiency early.
- Monitor plant health across large fields quickly and accurately.
Field Mapping & Planning
Generate 2D orthomosaic maps and 3D models of farmland to analyze terrain, drainage, and field variability.
Planting (Seeding Drones)
Some drones can seed cover crops or spray granules, reducing labor and equipment costs.
Precision Spraying
Apply fertilizers, pesticides, or herbicides only where needed using variable rate spraying, reducing chemical use and environmental impact.
Irrigation Management
- Detect areas with uneven water distribution using thermal cameras.
- Prevent overwatering or drought stress through real-time data.
Livestock Monitoring
Track herd movement, fence lines, or remote grazing areas.
Use of Drones in Environmental Monitoring

Habitat and Wildlife Monitoring
Track animal populations, nesting sites, or habitat changes with minimal disturbance.
Forest Management
- Map forest cover, tree height, and biomass.
- Detect illegal logging or monitor reforestation projects.
Wetland & Waterway Analysis
Survey rivers, lakes, wetlands for erosion, pollution, or invasive species using RGB, thermal, or multispectral imaging.
Disaster Assessment
Quickly assess floods, wildfires, landslides, or oil spills to guide emergency response and recovery.
Air and Soil Quality Monitoring
Some advanced drones can carry sensors to detect air pollutants or soil contamination in industrial or agricultural zones.
Climate Change Research
- Collect long-term aerial data on glaciers, coastlines, forests, or agricultural trends to support environmental studies.
- Adds a professional and modern touch to marketing material.
Use of Drones in Public Safety & Emergency Response

Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Thermal imaging helps locate missing persons in forests, mountains, or disaster zones even in low light or at night.
- Cover large areas quickly, guiding ground teams precisely to the location.
Disaster Response & Damage Assessment
After floods, fires, earthquakes, or hurricanes, drones:
- Assess structural damage
- Map affected areas
- Identify blocked roads or stranded individuals
Help prioritize resource allocation and speed up recovery.
Firefighting
- Provide live aerial views of fire spread and hotspots using infrared cameras.
- Help incident commanders make real-time tactical decisions.
- Used in wildfire mapping, urban fires, and hazardous material response.
Law Enforcement
- Monitor crime scenes, protests, or large gatherings for public safety.
- Track suspects or fleeing vehicles with minimal risk.
- Gather aerial evidence during investigations or traffic reconstructions.
Crowd Monitoring and Event Security
- Observe crowd flow and detect bottlenecks, suspicious activity, or safety hazards during large events (marathons, parades, rallies).
- Improve perimeter security and coordination.
Hazardous Material (HAZMAT) Situations
- Fly drones into toxic or dangerous areas (e.g., chemical spills, radiation zones) to assess the situation safely.
- Use sensors or cameras to measure gas levels or heat signatures.
Accident Scene Mapping
- Quickly map crash sites using photogrammetry for documentation and investigation.
- Reduce road closures and traffic delays.
Hobbyists to Commercial use

Understand the Legal Requirements
In most countries (like the U.S., Canada, UK, etc.), commercial drone use is regulated separately from hobby use.
In the United States
- Pass the FAA Part 107 exam (Remote Pilot Certificate)
- Covers airspace rules, weather, safety procedures, and drone regulations.
- Must be renewed every 2 years.
- Register your drone for commercial use with the FAA.
- Follow Part 107 flight rules (e.g., fly below 400 ft, maintain line-of-sight, no flying over people without waivers).
Even if you fly as a side business, you’re considered commercial and must be certified.
Choose a Commercial Focus Area
Decide what type of commercial drone work you want to offer based on your skills and local demand:
Set Up a Business
Choose a name and register your business
Keep Learning & Growing
Take Drone training classes/courses.
Stay updated on new tech
Career switchers and Tech Enthusiasts
Personal Interest / Hobby
- Start flying drones recreationally.
- Learn basic flight skills, safety, and photography/videography.
- Engage in drone communities and forums.
Skill Building & Certification
- Take Drone training/courses
- Get licensed
Niche Exploration
Identify what area excites you most:
Portfolio & Freelance Work
Build a sample portfolio (demo projects, volunteer work).
Business or Employment
Start a drone services business or consulting agency.

